Post History
It is well known that it is difficult to filter the noise generated by switching power supplies, and this difficulty increases as the PSU is supposed to deliver large currents. For example, in a us...
#7: Post edited
- It is well known that it is difficult to filter the noise generated by switching power supplies, and this difficulty increases as the PSU is supposed to deliver large currents.
- For example, in a usual LC filter, the self may reach the saturation if a large current is passing through.
- I would like to know what techniques are usually used in large current capable switching PSU to filter the (high frequency) output ripple.
- To restrict the question:
- * I'm not interested in the 50Hz low frequency noise,
- * not interested in the EMI power line filtering,
- * not interested in proper use of ground planes, separation, minimizing area in current loops, not breaking current return paths, identifying high current flow paths and keeping them short and away from noise sensitive parts of the circuit and like.
- * I'm interested only in the output filter.
- <hr>
- <blockquote>
- You still need to focus your question though.
- </blockquote>
- This basic circuit is more or less what I had in mind:
- 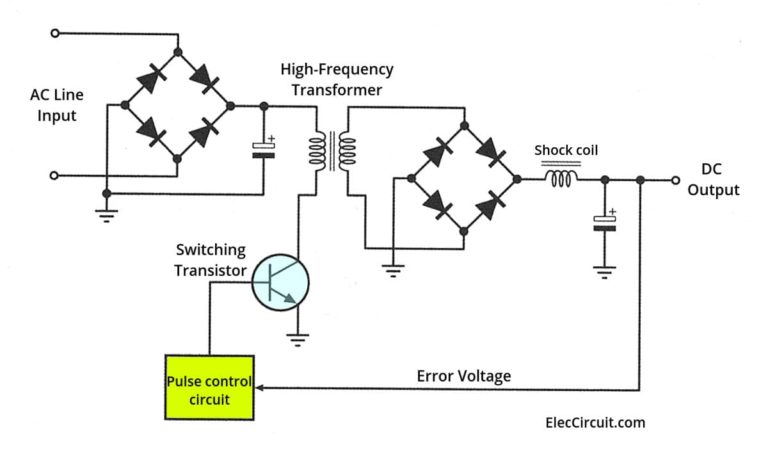
- What can be done to reduce the common mode noise?
- It is well known that it is difficult to filter the noise generated by switching power supplies, and this difficulty increases as the PSU is supposed to deliver large currents.
- For example, in a usual LC filter, the self may reach the saturation if a large current is passing through.
- I would like to know what techniques are usually used in large current capable switching PSU to filter the (high frequency) output ripple.
- To restrict the question:
- * I'm not interested in the 50Hz low frequency noise,
- * not interested in the EMI power line filtering,
- * not interested in proper use of ground planes, separation, minimizing area in current loops, not breaking current return paths, identifying high current flow paths and keeping them short and away from noise sensitive parts of the circuit and like.
- * I'm interested only in the output filter.
- <hr>
- <blockquote>
- You still need to focus your question though.
- </blockquote>
- This basic circuit is more or less what I had in mind:
- 
- A part of the original question has already been answered.
- So, to focus on the remaining points, my question is now:
- What can be done to reduce the common mode noise?
#6: Post edited
- It is well known that it is difficult to filter the noise generated by switching power supplies, and this difficulty increases as the PSU is supposed to deliver large currents.
- For example, in a usual LC filter, the self may reach the saturation if a large current is passing through.
- I would like to know what techniques are usually used in large current capable switching PSU to filter the (high frequency) output ripple.
- To restrict the question:
- * I'm not interested in the 50Hz low frequency noise,
- * not interested in the EMI power line filtering,
- * not interested in proper use of ground planes, separation, minimizing area in current loops, not breaking current return paths, identifying high current flow paths and keeping them short and away from noise sensitive parts of the circuit and like.
- * I'm interested only in the output filter.
- <hr>
- <blockquote>
- You still need to focus your question though.
- </blockquote>
This circuit is more or less what I had in mind:- 
- What can be done to reduce the common mode noise?
- It is well known that it is difficult to filter the noise generated by switching power supplies, and this difficulty increases as the PSU is supposed to deliver large currents.
- For example, in a usual LC filter, the self may reach the saturation if a large current is passing through.
- I would like to know what techniques are usually used in large current capable switching PSU to filter the (high frequency) output ripple.
- To restrict the question:
- * I'm not interested in the 50Hz low frequency noise,
- * not interested in the EMI power line filtering,
- * not interested in proper use of ground planes, separation, minimizing area in current loops, not breaking current return paths, identifying high current flow paths and keeping them short and away from noise sensitive parts of the circuit and like.
- * I'm interested only in the output filter.
- <hr>
- <blockquote>
- You still need to focus your question though.
- </blockquote>
- This basic circuit is more or less what I had in mind:
- 
- What can be done to reduce the common mode noise?
#5: Post edited
- It is well known that it is difficult to filter the noise generated by switching power supplies, and this difficulty increases as the PSU is supposed to deliver large currents.
- For example, in a usual LC filter, the self may reach the saturation if a large current is passing through.
- I would like to know what techniques are usually used in large current capable switching PSU to filter the (high frequency) output ripple.
- To restrict the question:
- * I'm not interested in the 50Hz low frequency noise,
- * not interested in the EMI power line filtering,
- * not interested in proper use of ground planes, separation, minimizing area in current loops, not breaking current return paths, identifying high current flow paths and keeping them short and away from noise sensitive parts of the circuit and like.
- * I'm interested only in the output filter.
Also, an example with a schematic showing the connections and where is the feedback wire connected will be appreciated.
- It is well known that it is difficult to filter the noise generated by switching power supplies, and this difficulty increases as the PSU is supposed to deliver large currents.
- For example, in a usual LC filter, the self may reach the saturation if a large current is passing through.
- I would like to know what techniques are usually used in large current capable switching PSU to filter the (high frequency) output ripple.
- To restrict the question:
- * I'm not interested in the 50Hz low frequency noise,
- * not interested in the EMI power line filtering,
- * not interested in proper use of ground planes, separation, minimizing area in current loops, not breaking current return paths, identifying high current flow paths and keeping them short and away from noise sensitive parts of the circuit and like.
- * I'm interested only in the output filter.
- <hr>
- <blockquote>
- You still need to focus your question though.
- </blockquote>
- This circuit is more or less what I had in mind:
- 
- What can be done to reduce the common mode noise?
#4: Post edited
- It is well known that it is difficult to filter the noise generated by switching power supplies, and this difficulty increases as the PSU is supposed to deliver large currents.
- For example, in a usual LC filter, the self may reach the saturation if a large current is passing through.
I would like to know what techniques are usually used in large current capable switching PSU to filter the (high frequency) ripple (I'm not interested in the 50Hz low frequency noise). Also, an example with a schematic showing the connections and where is the feedback wire connected will be appreciated.
- It is well known that it is difficult to filter the noise generated by switching power supplies, and this difficulty increases as the PSU is supposed to deliver large currents.
- For example, in a usual LC filter, the self may reach the saturation if a large current is passing through.
- I would like to know what techniques are usually used in large current capable switching PSU to filter the (high frequency) output ripple.
- To restrict the question:
- * I'm not interested in the 50Hz low frequency noise,
- * not interested in the EMI power line filtering,
- * not interested in proper use of ground planes, separation, minimizing area in current loops, not breaking current return paths, identifying high current flow paths and keeping them short and away from noise sensitive parts of the circuit and like.
- * I'm interested only in the output filter.
- Also, an example with a schematic showing the connections and where is the feedback wire connected will be appreciated.
#3: Post edited
- It is well known that it is difficult to filter the noise generated by switching power supplies, and this difficulty increases as the PSU is supposed to deliver large currents.
- For example, in a usual LC filter, the self may reach the saturation if a large current is passing through.
I would like to know what techniques are usually used in switching PSU to filter the (high frequency) ripple (I'm not interested in the 50Hz low frequency noise). Also, an example with a schematic showing the connections and where is the feedback wire connected will be appreciated.
- It is well known that it is difficult to filter the noise generated by switching power supplies, and this difficulty increases as the PSU is supposed to deliver large currents.
- For example, in a usual LC filter, the self may reach the saturation if a large current is passing through.
- I would like to know what techniques are usually used in large current capable switching PSU to filter the (high frequency) ripple (I'm not interested in the 50Hz low frequency noise). Also, an example with a schematic showing the connections and where is the feedback wire connected will be appreciated.
#2: Post edited
filtering the high frequency noise in switching PSU
- Filtering the high frequency noise in switching PSU
#1: Initial revision
filtering the high frequency noise in switching PSU
It is well known that it is difficult to filter the noise generated by switching power supplies, and this difficulty increases as the PSU is supposed to deliver large currents. For example, in a usual LC filter, the self may reach the saturation if a large current is passing through. I would like to know what techniques are usually used in switching PSU to filter the (high frequency) ripple (I'm not interested in the 50Hz low frequency noise). Also, an example with a schematic showing the connections and where is the feedback wire connected will be appreciated.


















