Post History
A MOSFET has its gate, source and drain on the top side [1]. These structures are sitting on top of the substrate, which is also called body or bulk. The source and drain are n-doped, while the...
#3: Post edited
- 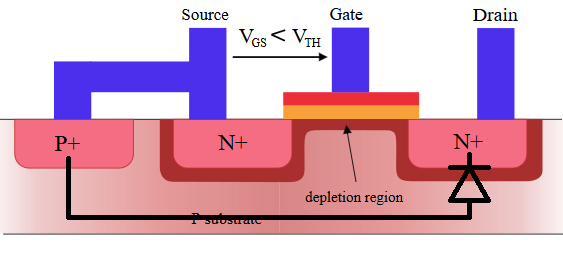
A MOSFET has its gate, source and drain on the top side <sup>1</sup>. These structures are sitting on top of the substrate, which is also called body or bulk. The source and drain are n-doped, while the body is p-doped.<sup>2</sup> There are p-n junctions between body and drain, and between bulk and source. These p-n junctions behave like diodes. If the p-doped body is at a higher potential than the n-doped source or drain, then an unwanted current will flow from body into source.- To avoid that, we need to keep the the p-n junctions reverse-biased always. We need to bias the body to a voltage that's lower than source and drain, or equal to source and drain. The cheap way to achieve that is to connect the body to the source, and design the rest of the circuit such that the source voltage always lower or equal to the drain voltage. The p-n junction between the body and the drain becomes the junction between the source and the drain. That is the body diode.
- In principle, a MOSFET is a four-terminal device. Inside ICs sometimes, the MOSFET body may be connected to a voltage that's lower than source and drain, instead of connecting body to source. Discrete MOSFETs with the fourth pin for a body connection do exist, although they are rare.
<sup>1</sup> I'm using a lateral MOSFET as an example. The discussion is similar for a vertical MOSFET.<sup>2</sup> I'm using an N-channel MOSFETs as an example. The same discussion applies to a P-channel MOSFET, except everything is inverted.
- 
- A MOSFET has its gate, source and drain on the top side [^1]. These structures are sitting on top of the substrate, which is also called body or bulk. The source and drain are n-doped, while the body is p-doped.[^2] There are p-n junctions between body and drain, and between bulk and source. These p-n junctions behave like diodes. If the p-doped body is at a higher potential than the n-doped source or drain, then an unwanted current will flow from body into source.
- To avoid that, we need to keep the the p-n junctions reverse-biased always. We need to bias the body to a voltage that's lower than source and drain, or equal to source and drain. The cheap way to achieve that is to connect the body to the source, and design the rest of the circuit such that the source voltage always lower or equal to the drain voltage. The p-n junction between the body and the drain becomes the junction between the source and the drain. That is the body diode.
- In principle, a MOSFET is a four-terminal device. Inside ICs sometimes, the MOSFET body may be connected to a voltage that's lower than source and drain, instead of connecting body to source. Discrete MOSFETs with the fourth pin for a body connection do exist, although they are rare.
- [^1]: I'm using a lateral MOSFET as an example. The discussion is similar for a vertical MOSFET.
- [^2]: I'm using an N-channel MOSFETs as an example. The same discussion applies to a P-channel MOSFET, except everything is inverted.
#2: Post edited
A MOSFET has its gate, source and drain on the top side <sup>1</sup>. These structures are sitting on top of the substrate, which is also called body or bulk. The source and drain are n-doped, while the body is p-doped.<sup>2</sup> There are p-n junctions between body and drain, and between bulk and source. These p-n junctions behave like diodes. If the p-doped body is at a higher potential than the n-doped source or drain, then an unwanted current will flow from body into source.- 
To avoid that, we need to keep the the p-n junctions reverse-biased. We need to bias it to a voltage that's lower than source and drain, or equal to source and drain. The cheap way to achieve that is to connect the body to the source, and keep the source voltage always lower or equal to the drain voltage. The p-n junction between the body and the drain becomes the junction between the source and the drain. That is the body diode.In principle, a MOSFET is a four-terminal device, because body is exposed on the top side. Inside ICs sometimes, the MOSFET body may be connected to a voltage that's lower than source and drain, instead of connecting body to source. Discrete MOSFETs with the fourth pin for a body connection do exist, although they are rare.<sup>1</sup> I'll use a lateral MOSFET as an example. The discussion is similar for a vertical MOSFET.- <sup>2</sup> I'm using an N-channel MOSFETs as an example. The same discussion applies to a P-channel MOSFET, except everything is inverted.
- 
- A MOSFET has its gate, source and drain on the top side <sup>1</sup>. These structures are sitting on top of the substrate, which is also called body or bulk. The source and drain are n-doped, while the body is p-doped.<sup>2</sup> There are p-n junctions between body and drain, and between bulk and source. These p-n junctions behave like diodes. If the p-doped body is at a higher potential than the n-doped source or drain, then an unwanted current will flow from body into source.
- To avoid that, we need to keep the the p-n junctions reverse-biased always. We need to bias the body to a voltage that's lower than source and drain, or equal to source and drain. The cheap way to achieve that is to connect the body to the source, and design the rest of the circuit such that the source voltage always lower or equal to the drain voltage. The p-n junction between the body and the drain becomes the junction between the source and the drain. That is the body diode.
- In principle, a MOSFET is a four-terminal device. Inside ICs sometimes, the MOSFET body may be connected to a voltage that's lower than source and drain, instead of connecting body to source. Discrete MOSFETs with the fourth pin for a body connection do exist, although they are rare.
- <sup>1</sup> I'm using a lateral MOSFET as an example. The discussion is similar for a vertical MOSFET.
- <sup>2</sup> I'm using an N-channel MOSFETs as an example. The same discussion applies to a P-channel MOSFET, except everything is inverted.
#1: Initial revision
A MOSFET has its gate, source and drain on the top side <sup>1</sup>. These structures are sitting on top of the substrate, which is also called body or bulk. The source and drain are n-doped, while the body is p-doped.<sup>2</sup> There are p-n junctions between body and drain, and between bulk and source. These p-n junctions behave like diodes. If the p-doped body is at a higher potential than the n-doped source or drain, then an unwanted current will flow from body into source.  To avoid that, we need to keep the the p-n junctions reverse-biased. We need to bias it to a voltage that's lower than source and drain, or equal to source and drain. The cheap way to achieve that is to connect the body to the source, and keep the source voltage always lower or equal to the drain voltage. The p-n junction between the body and the drain becomes the junction between the source and the drain. That is the body diode. In principle, a MOSFET is a four-terminal device, because body is exposed on the top side. Inside ICs sometimes, the MOSFET body may be connected to a voltage that's lower than source and drain, instead of connecting body to source. Discrete MOSFETs with the fourth pin for a body connection do exist, although they are rare. <sup>1</sup> I'll use a lateral MOSFET as an example. The discussion is similar for a vertical MOSFET. <sup>2</sup> I'm using an N-channel MOSFETs as an example. The same discussion applies to a P-channel MOSFET, except everything is inverted.


















