Post History
That fourth connection is the bulk/body/substrate connection: - Image from here. On a normal 3 terminal MOSFET the "body" is connected to the source. On your device, the 3 n-channel MOSFETs shar...
#3: Post edited
- That fourth connection is the bulk/body/substrate connection: -
- 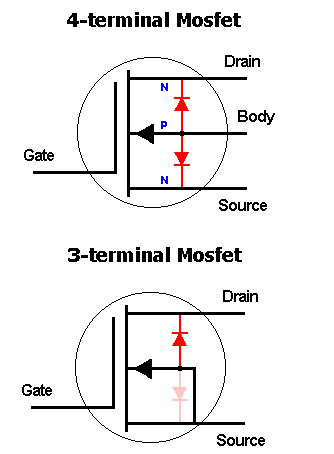
Image from [here](http://www.muzique.com/news/mosfet-body-diodes/). On a normal 3 terminal MOSFET the "body" is connected to the source. On your device, the 3 n-channel MOSFETs share a common bulk pin that should usually be connected to the most negative voltage of your circuit (quite often 0 volts or GND).
- That fourth connection is the bulk/body/substrate connection: -
- 
- Image from [here](http://www.muzique.com/news/mosfet-body-diodes/). On a normal 3 terminal MOSFET the "body" is connected to the source. On your device, the 3 n-channel MOSFETs share a common bulk pin that should usually be connected to the most negative voltage of your circuit (quite often 0 volts or GND).
- $$$$
- Internally, the body/bulk connection is shown in the picture below: -
- 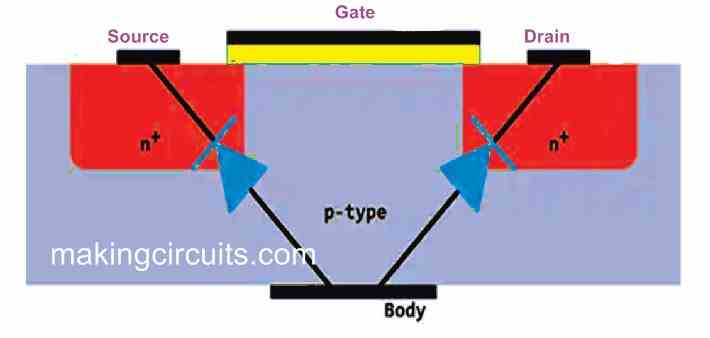
- As the gate voltage rises positively with respect to the source, the p type material between drain and source inverts to n type material and forms a conducting channel.
#2: Post edited
That fourth connection is the bulk/body connection: -- 
Image from [here](http://www.muzique.com/news/mosfet-body-diodes/). On a normal 3 terminal MOSFET the "body" is connected to the source.
- That fourth connection is the bulk/body/substrate connection: -
- 
- Image from [here](http://www.muzique.com/news/mosfet-body-diodes/). On a normal 3 terminal MOSFET the "body" is connected to the source. On your device, the 3 n-channel MOSFETs share a common bulk pin that should usually be connected to the most negative voltage of your circuit (quite often 0 volts or GND).


















